Walk and Roll Cities: a transformation towards people-centred streets
Edited on
30 March 2022Meet the URBACT cities exploring links between mobility and public space to promote sustainable, inclusive, attractive urban areas.

In recent decades, mobility in cities has become strongly dominated by cars. The moving and parking of quickly expanding numbers of cars led to the shrinkage of public space available for residents.
 In order to reverse the dominance of cars, since the 2010s many European cities have started to explore new measures to deter the use and storing of cars on streets, and support alternative uses of public spaces. Three ongoing URBACT Action Planning Networks address these issues: Space4People, concentrating on parking management and pedestrianisation; Thriving Streets, on streets as public spaces and placemaking; and RiConnect, dealing with the links between regional and local aspects of mobility infrastructures.
In order to reverse the dominance of cars, since the 2010s many European cities have started to explore new measures to deter the use and storing of cars on streets, and support alternative uses of public spaces. Three ongoing URBACT Action Planning Networks address these issues: Space4People, concentrating on parking management and pedestrianisation; Thriving Streets, on streets as public spaces and placemaking; and RiConnect, dealing with the links between regional and local aspects of mobility infrastructures.
Under the banner of #WalkAndRollCities, these three URBACT city networks decided to set up a collaboration to explore the links between mobility and transport and public space use, and collect good practices on progressive changes in cities. Set to run until summer 2022, their joint activities include a series of three seminars, and a LinkedIn group for case studies and debates.
The first URBACT #WalkAndRollCities webinar
The first webinar of this collaboration was held on 29 November 2021. In his keynote presentation, Tiago Lopes Farias, CEO at CARRIS – the Lisbon Municipal Bus and Tram Operator, and associate professor at Instituto Superior Técnico, University of Lisbon (PT), highlighted Lisbon’s main efforts. The starting point was the strengthening of powers at metropolitan level – stretching over 18 municipalities, and 2.9 million people, only 0.5 million of whom live in Lisbon itself. This enabled new efforts to streamline the public transport system across the whole metropolitan area, starting with a ticketing reform to introduce a new, integrated tariff model. This was followed by efforts to establish a joint public transport company for the whole area.
Cities from the URBACT networks Space4People, Thriving Streets, and RiConnect have been sharing their experiences of strengthening urban sustainability by giving more ground to active mobility modes and enhancing the people-friendly use of public spaces. Here are a few interesting examples presented during the recent webinar. (See the #WalkAndRollCities LinkedIn group for more details.)
Arad (RO) implemented pilot pedestrian interventions on one of the main boulevards of the city. The majority of people supported the idea to expand walking areas, mainly as a leisure form, especially on weekends or during warmer weather. The city recognised the importance of building trust through active communication, complemented by delivery, in the form of pilot interventions.
Bielefeld (DE) focused on parking management, to give public space back to people, reducing street parking and changing vehicle access regulations to the city centre. The five-month period of idea raising was followed by a five-month-long testing phase, during which opinions about the pilot projects were collected. The process will end with a four-month evaluation and decision-making phase.
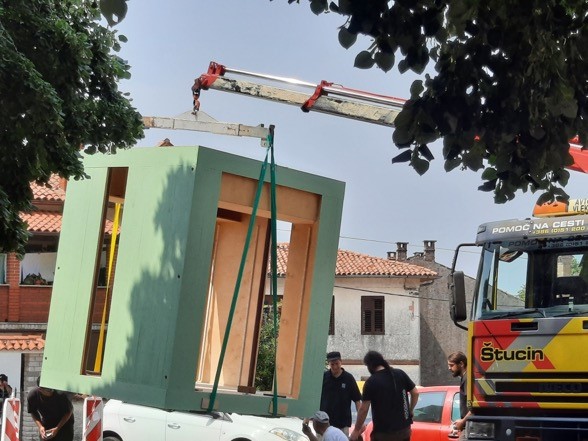 |
| Nova Gorica: removing a car, installing a kiosk |
Nova Gorica (SI) aimed to restructure a square in the historic core area of the city by removing parking spaces while installing a pop-up kiosk to enhance public activities – as shown in the photo. A detailed insight into the issue of space only became possible when the vision-building period was followed with a concrete action, making the idea visible for residents. The pilot intervention sparked heavy debates between residents, which led to further changes being made.
Antwerp (BE) wanted to stimulate change in a peripheral neighbourhood where the share of younger people, preferring bikes instead of car use, is increasing. The temporary installations of the city, aiming to create more space for pedestrians and slow down car traffic, however, were not prepared and discussed properly. The municipality has learnt a lot from this failed experiment: how temporary interventions should be prepared; what needs have to be taken into account; and how important it is to engage residents fully in discussions, by municipal employees who get enough resources to organise that.
The Métropole du Grand Paris (FR) is aiming to calm traffic on a four-lane national road running through the centre of a peripheral municipality. The attempts to ‘localise’ the road by creating new crossings and green spaces will hopefully incentivise private actors to invest in housing and prompt the regeneration of heritage buildings. For the idea to succeed, coordination between different levels of governance is of crucial importance.
Transport for Greater Manchester (UK) aims for similar interventions in a peripheral sub-centre of the Greater Manchester metropolitan area. The aim is to ‘humanise’ the entry area of a motorway by improving the crossings, creating streets for all, and introducing a quality bus service. Manchester hopes that this will lead to longer-term changes in the mobility behaviour of local residents.
Then came COVID
All these efforts in URBACT cities started a few years ago. Then suddenly, in March 2020, Covid-19 hit. The quickly introduced lockdown measures brought dramatic changes in the first months, which planners couldn’t have dreamt of earlier: huge decreases in car use, alongside much more intensive use of public spaces. In some cases, areas originally used by cars were even ‘stolen’ for temporary measures.
A few months later, however, a very unfortunate rearrangement started: the use of cars increased again, and in many cities reached higher levels than before the pandemic – not least because people continued to avoid public transport. As a result, pressure was growing to eliminate new measures favouring walking and cycling in cities. Municipalities now face the dilemma of how to react to the anger of car drivers while listening to the (often less well-articulated) opinion of pedestrians and cyclists who are satisfied with the public places which were expanded for their use.
 |
| In Budapest, one of the newly installed bike lanes had to be redirected to the pavement in order to give back partially a lane to car drivers. |
Claus Köllinger, Lead Expert of the Space4People network, told the URBACT #WalkAndRollCities webinar: “Due to increasing car use, if nothing changes in centres, depopulation and retail extinction can happen. There are many alternative futures for central areas possible, such as Disneyland, large gastronomy bars, entertainment centres, or good mix of different functions. Wise interventions are needed to favour the last option, and this requires to push back car access to the central areas.”
Positive visions for mobility and public space use in the post-Covid city
Over the course of the webinar, important statements were articulated towards a positive vision for the post-Covid city. As Béla Kézy, Lead Expert of the Thriving Streets network, said: “Mobility – how far you can go in a given amount of time – should be replaced by Access – how much you can get in a given amount of time. The '15-minute city’ idea aims to provide access instead (or besides) mobility, for which you need proximity, diversity, density, ubiquity.”
There are no standard solutions for changing existing neighbourhoods along these principles; the concrete needs of people always have to be studied and understood first. It might be useful to ease strict zoning regulations – such as allowing a café to open in a residential area – and handing over places to community functions, for example opening up existing public buildings in the evenings and putting in new community buildings wherever possible.
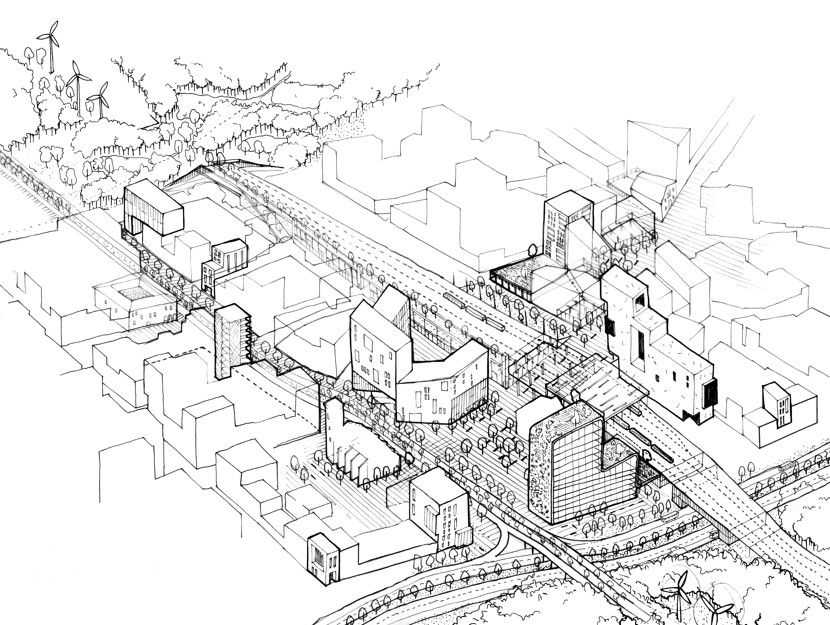 |
| Rebuilding a transfer station area |
Roland Krebs, Lead Expert of the RiConnect network, emphasised the need for integrated solutions. He said: “Old infrastructures, which were once in the centre of activities, are overdone by new layers, totally changing the earlier important places, making these peripheral and through-locations. Over time, transfer places become monofunctional, losing identity and human scale. The task is to re-arrange earlier-built infrastructures by new uses, urban intensification and urban regeneration, assuring more mixed functions than just stations for exchange between mobility modes. In peripheral areas, all this needs strong multi-level government cooperation.”
In his keynote address, Tiago Lopes Farias addressed the question of how to build on the pandemic-created momentum of changes towards less car dominant mobility and public space use, by raising new aspects for consideration:
1. Customer needs and mobility patterns will change due to teleworking, e-commerce, growing expectations of customers due to accelerated digitalisation, increased attention to the ’local’ (15-minute city), safety concerns.
2. New mobility players are coming in, and an innovative and dynamic ecosystem will be built up, based on more electrified, shared technologies. All these need space and raise the challenge of how they can be connected.
3. All this leads to the scarcity of space: how to better manage urban space and mobility services towards more sustainable cities. Where to put the bike-share rack, the e-roller rack within the same physical space? To whom to give parking space: residents, long-term visitors, loading of goods? But first other questions have to be asked: is the space for parking, or a bus lane, or pedestrians…?
4. Added to all that, there is a growing pressure to reduce our carbon footprint. In Lisbon, the bus fleet will be zero emission by 2040… the first 15 electric buses are already running, but depos also have to be changed…
Tiago Lopes Farias said: “We need to change, adapt how we live, plan, manage our lives. This means that also mobility patterns have to be changed. But it should be ensured that public transport remains the backbone of urban mobility, and that cities remain the centres of urban areas.”
Serious barriers endangering sustainability changes
The first webinar of URBACT Walk And Roll Cities ended with an emphasis on the need to connect changes in mobility and public space use to each other. The leading role has to be played by the public sector, based on the cooperation of municipalities in the metropolitan areas, in partnership with private actors and in active consultation with the population.
It is, however, not at all easy to reach the envisioned changes. There are already signs in many cities of an approaching financial austerity, which would heavily affect services, public transport amongst the first. If the next decision has to be about which line to shut down or how to save money by decreasing the frequency of services, little room will remain for innovative ideas about the future. Thus, financing and resourcing of mobility services is one of the most important questions for the near future. This will be the topic of the next URBACT #WalkAndRollCities webinar, planned for the first quarter of 2022.
All the materials of the first webinar will be available on the URBACT Walk And Roll Cities LinkedIn group, open to all. Join up to discover new information about Walk And Roll Cities, and contribute with innovative ideas for improving mobility and public space in towns and cities across the EU.
You can also donwload the PowerPoint presentation on the event's page.
 Submitted by ivan.tosics on
Submitted by ivan.tosics on




