Social Impact Bonds: the secret tool for effective public services?
Edited on
07 February 2020In times of financial constraints, total government expenditures on public services are decreasing, while citizens expect more and more effective services. Social Impact Bonds may be the tool for providing funds and overcoming short-term focus, fragmentation of services and lack of innovation.

Total government expenditure in the EU-28 decreased from 50% of GDP to 45.8% between 2009 and 2017. Similarly, local government spending fell from 12% of GDP to 11% between 2009 and 2015. Still, demands on services have remained intense, and spending on social protection as a proportion of total expenditure increased from 38.8% to 41.2% and spending on health increased from 14.7% to 15.3% in the same period. Cities provide many of those services, -and doing so while running on tight budgets causes significant strain.
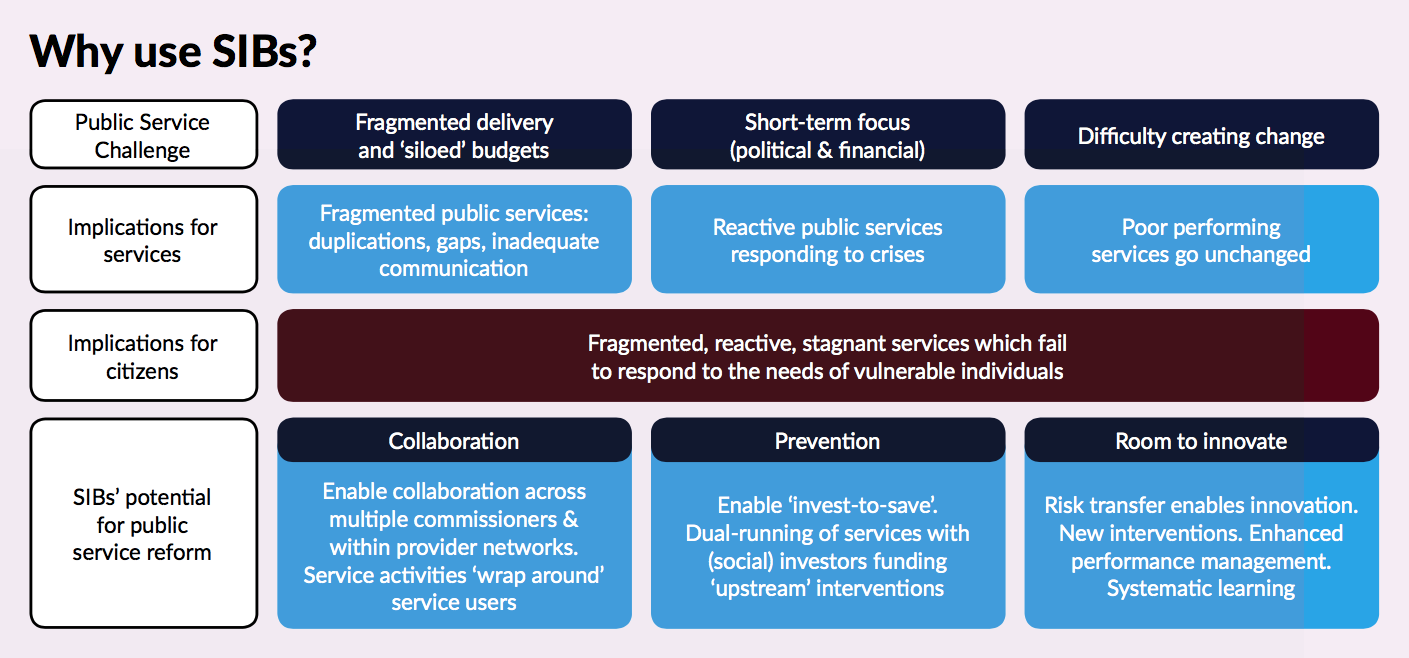
Besides shrinking budgets, providing effective services fail because they are often split between different departments, and a holistic approach is lacking. Cities are pressured to allocate resources to solving crisis-point situations instead of spending on prevention. In such a context, decision-makers opt for the business-as-usual approach without risking relatively unknown interventions that have a severe upfront cost.
In the meantime, the idea of ‘socially responsible’ or ‘impact investment’ is emerging amidst a low interest rate environment. The trend of investing in the social environment has become a way for investors to give back to the community. Very often, companies are trying to expand their social responsibility. As a result, a growing number of investors are looking for forms of impact investments as a way to stand up for their beliefs and also make a profit.
The relatively new tool for bringing together the investor and the public sector is the Social Impact Bond (SIB). It is a contract whereby the public authority or governing authority pays for better social outcomes in certain areas and passes the savings achieved to investors. Unlike a bond, the repayment and the return on investment are contingent upon the achievement of desired social outcomes. If a project meets the pre-agreed results, i.e. an improved social outcome that generates a cost-saving, the government (this can be local or national) pays the investors. If a project does not achieve its contracted results, the investors lose their money, and the government pays nothing.
1. Figure: Social Impact Bonds’ theory of change. Source: University of Oxford, Government Outcomes Lab - An Intro to SIB.
A Social Impact Bond may have many beneficial effects for cities, as Government Outcomes Lab states in its Evidence Report titled ‘Building the tools for public services to secure better outcomes’. It encourages collaboration by building on cross-sector expertise and bringing together multiple commissioners and multiple providers. It unlocks future savings by investing more up-front, enabling cities to focus on prevention and early intervention services that might otherwise not get funded. A SIB may inspire innovation by allowing new interventions and more flexibility. It also levels the field for involving voluntary, community and social enterprise organisations. Last but not least, a SIB can improve performance management and provides a better quality of evidence.
Many critics are contesting these benefits, saying that a SIB does not encourage genuine innovation. Investors will be looking for low-risk models that have been proven to deliver, as they want their money back. Moreover, a SIB is expensive to develop and leads to the financialization of the public sector, which is – for many - incompatible with the public service ethos.
With evidence on both sides, Social Impact Bonds need more experimentation and evaluation. And despite these circumstances of austerity, some cities try to use the momentum to shift their approach towards this new tool. That is why 10 cities joined their forces in URBACT SIBdev Network to jointly explore how Social Impact Bonds, can improve public service delivery. The tool and the URBACT methodology, namely coproduction through multi-stakeholder local support groups and the development of local action plans fit perfectly.
The network will examine service delivery concerning employment, ageing and immigration. Employment is an obvious choice since SIB is particularly well-suited to it, as demonstrated by the fact that it is the most common type of SIB worldwide. Ageing is the most massive pressure on social spending in Europe and affects a growing number of people, while immigration is the primary concern at the EU level (according to Eurobarometer).
Is SIB going to be the new secret tool for providing adequate public services? Maybe it will be, maybe not. But it certainly is a promising new form of commissioning social services. If you are interested in Finance and/or Social Services, follow URBACT SIBdev Network to learn about how SIB might work for you!

1. Photo: Harrie Lambrichts
 Submitted by Zsolt Séra on
Submitted by Zsolt Séra on




