The urban dimension of smart specialisation: building a two-way bridge
Edited on
24 June 2019Smart specialisation and its related methodology known as Research and Innovation Strategy for Smart Specialisation (RIS3) have been assessed as “the most comprehensive industrial policy experience being implemented in contemporary Europe”. In this context, what is the role to be played by cities? Right now, at the time of implementation, a number of major cities feel they have much to contribute in moving RIS3 visions and roadmaps forward. So, what are the pathways and frameworks to enhance better alignment between regions and cities with regard to existing RIS3 strategies? What is the urban dimension of smart specialisation? This article brings some insights to these questions.

Smart specialisation adds two key values to previous Regional Innovation Strategies in the EU, namely:
- the value of prioritizing (of making smart choices) and
- how such prioritization should be done and kept current through a collaborative process that involves as many stakeholders from the triple/quadruple helix as possible, in particular research centres, leading firms and entrepreneurs in a process that is now called “entrepreneurial discovery”.
Since RIS3 was fixed as an ex-ante conditionality for EU regions and member states to get ERDF funding for their Operational Programmes on innovation, smart specialization has entered the mainstream vocabulary in business-led economic development.
InFocus-Smart Specialisation at City Level is a pioneering URBACT network that brings a city perspective to this new policy concept, pursuing a double aim.
Firstly, re-invigorating the urban agenda on economic development by means of smart specialization as an overarching approach. That is, testing how this concept can foster and refine the work cities and their stakeholders are doing (or can do) in four key areas: cluster development, entrepreneurship, workspace provision and investment attraction.
Secondly, making a bridge with the existing RIS3 strategies at regional level, which is basically a matter of multi-level governance.
Why both cities and RIS3 leading authorities need to be involved
Tackling the question of effective city-to-region articulation with regard to smart specialisation presents a precious opportunity to raise the status of some innovative cities in the field of industrial and innovation policies, especially given the main role major cities play in today´s global competition. But are cities ready to take full advantage of smart specialisation and RIS3?
The fact is that for many cities it seems like RIS3 has little to do with them. This misunderstanding arises from the RIS3 elaboration process, when cities were mostly approached within a conventional public consultation logic, rather than in the spirit of real co-production. As a result, the idea of smart specialisation is still barely assimilated at local level, and there is much to do to raise awareness on the meaning and potential impact of smart specialisation.
 Another powerful reason to draw the attention on the city-to-region articulation with regard to smart specialisation is that RIS3 implementation has just begun. It is a significant challenge, bigger than RIS3 design, where all efforts, at different scales, should be activated. In this respect local and metropolitan authorities could help to embed RIS3 strategies properly. As a territorial innovation policy at regional/national level, RIS3 should have a more consistent and explicit territorial strategy. The InFocus network is working to fill that gap, in close collaboration with the S3 Platform, which is the unit created by the European Commission to assist regions and member states on smart specialisation.
Another powerful reason to draw the attention on the city-to-region articulation with regard to smart specialisation is that RIS3 implementation has just begun. It is a significant challenge, bigger than RIS3 design, where all efforts, at different scales, should be activated. In this respect local and metropolitan authorities could help to embed RIS3 strategies properly. As a territorial innovation policy at regional/national level, RIS3 should have a more consistent and explicit territorial strategy. The InFocus network is working to fill that gap, in close collaboration with the S3 Platform, which is the unit created by the European Commission to assist regions and member states on smart specialisation.
Furthermore, some innovative cities and metropolitan areas in Europe are currently promoting ambitious transforming agendas, e.g. Next Economy roadmap in Rotterdam inspired by Jeremy Rifkin´s ideas, and Bilbao Next Lab which is presented as an “action-research approach for the economic transformation of Bilbao”. Thus, RIS3 strategies (which are themselves presented as policy frameworks for economic transformation) and these visionary city roadmaps might become mutually reinforcing if well connected and aligned.
Building the bridge
So, what can you do to properly align your work agenda as a city to your regional smart specialisation strategy? How can you make the most of the powerful concept of smart specialization to refine your own urban agenda in economic development? We, in InFocus, have gathered a number of experiences as follows, inside and outside the network, mostly, still at an exploratory stage which can provide a path to tackle these questions.
Integrated urban development initiatives (art. 7 ERDF).
In the context of integrated and sustainable urban development strategies (article 7 of ERDF), the DG for Regional and Urban Policy of the European Commission is encouraging cities to bridge with their existing RIS3 strategies at regional/national level. For instance, the Integrated Territorial Investment (ITI) now underway in the urban agglomeration of Ostrava (CZ) is organized in three strategic goals (the “3E” Employment, Entrepreneurship and Environment) and eleven specific objectives. One these objectives, as part of the strategic goal on Entrepreneurship is specifically dedicated to “implement activities to support smart specialization strategies for Moravian-Silesian Region”.
New metropolitan agendas as windows of opportunity.
 Territorial reform in some member states, like France and Italy, has led to urban policies in major cities being re-scaled up to the metropolitan level. In urban agglomerations like Bordeaux, Grenoble and Turin (all of them InFocus partners) new policy-mixes for new ambitions are in progress, and the smart specialisation approach will certainly play a significant role. The former province of Turin, now turned into new metropolitan authority (Cittá Metropolitana di Torino, including 315 municipalities and a population of 2.3 million - 890,000 in the Municipality of Torino) is facing the challenge of both horizontal and vertical multi-level governance. At this juncture, the idea of smart specialization has great potential to work as a driver to promote more articulation and cohesion. That is, smart specialization as a tool to create more alignment and focus among all the initiatives within the metropolitan area on cluster development, entrepreneurship, attraction of investment, etc.
Territorial reform in some member states, like France and Italy, has led to urban policies in major cities being re-scaled up to the metropolitan level. In urban agglomerations like Bordeaux, Grenoble and Turin (all of them InFocus partners) new policy-mixes for new ambitions are in progress, and the smart specialisation approach will certainly play a significant role. The former province of Turin, now turned into new metropolitan authority (Cittá Metropolitana di Torino, including 315 municipalities and a population of 2.3 million - 890,000 in the Municipality of Torino) is facing the challenge of both horizontal and vertical multi-level governance. At this juncture, the idea of smart specialization has great potential to work as a driver to promote more articulation and cohesion. That is, smart specialization as a tool to create more alignment and focus among all the initiatives within the metropolitan area on cluster development, entrepreneurship, attraction of investment, etc.
RIS3 authorities taking the lead to engage with funding.
Catalonia is organising sub-regional initiatives called Territorial Specialisation and Competitiveness Projects (PECTs) to articulate to regional RIS3 (RIS3CAT). PECTs are innovation-oriented integrated initiatives that are developed by a partnership of minimum four entities led by a public administration at local, county or province level. On a yearly basis, the regional government launches competitive calls for funding PECTs, which are actually addressed as RIS3 delivery tools. The budget for the 2016 call was 50 million Euros to cover 50% of the approved projects, of which 20M went to Barcelona metropolitan area and 30M to the rest. In this context, Barcelona has drafted the strategy RIS3BCN Growth, which is explicitly presented as an alignment to RIS3CAT.
Matching priority domains from regional and local levels.
This might be a first step a city takes to align itself to RIS3 at region/country level. For example, Sevilla (ES) started a bridging process of this kind in 2016 with a comparative analysis between the RIS3 priorities set at the regional level and the city´s own industrial specialisations, dynamics and assets. This analysis led to a strategic vision, the identification of sectoral priorities and policy recommendations in order to give more focus to a number of existing working areas at city level, such as entrepreneurship, workspace provision and city branding. The idea is not so much to confront vertical priorities set at both regional and local levels, but to align the existing cluster dynamics at city level and cluster initiatives, if any, to the priority domains already agreed at regional/national RIS3 level.
Re-thinking the policy-mix at city/metro level in a way that actively contributes to RIS3 roadmaps.
RIS3 type strategies consist of the definition of a specialisation pattern, together with a set of aligned horizontal policies, such as research and innovation, entrepreneurship, cluster development, internationalisation, etc. Smart specialisation can be seen as an organisational driver aimed to promote growth within a place-based, comprehensive long-term strategy to sustain competitive advantages and help to build new ones, as well as to accelerate the necessary structural changes.
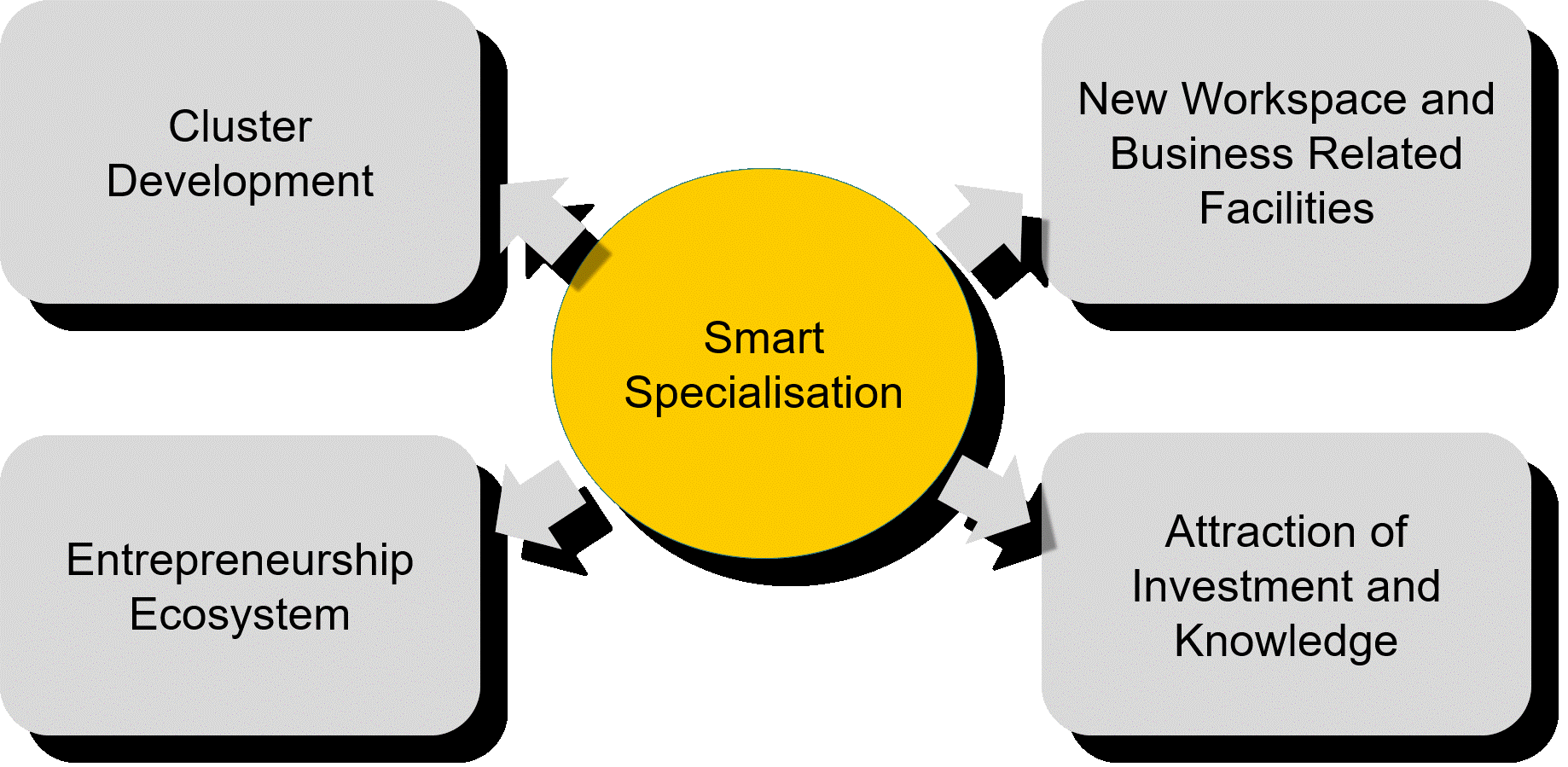 Therefore, changing or just influencing the strategic agenda from existing operators is one of the main paths to move RIS3 from strategy into action. When that existing operator is a local agency of a major city with an extensive background in economic development, such a delivery channel may work as a strategic lever for success. Furthermore, in some cases, that kind of public or private-public body in charge of economic development at city level is already working actively in areas like workspace provision or inward investment and talent attraction. These work areas cannot easily be found in most of RIS3 designs at national/regional level, so the result is a refinement of the RIS3 conventional policy-mix. This is why the challenge of connecting RIS3 to the city should be addressed as a two-way bridge.
Therefore, changing or just influencing the strategic agenda from existing operators is one of the main paths to move RIS3 from strategy into action. When that existing operator is a local agency of a major city with an extensive background in economic development, such a delivery channel may work as a strategic lever for success. Furthermore, in some cases, that kind of public or private-public body in charge of economic development at city level is already working actively in areas like workspace provision or inward investment and talent attraction. These work areas cannot easily be found in most of RIS3 designs at national/regional level, so the result is a refinement of the RIS3 conventional policy-mix. This is why the challenge of connecting RIS3 to the city should be addressed as a two-way bridge.
In any case, cities can take advantage of the smart specialisation concept to strengthen their own policy-mix on business-led economic development. In the frame of the InFocus network, the City of Ostrava is drafting an Integrated Action Plan oriented to talent attraction and retention. To do so, they are using the range of priority knowledge/productive domains set at RIS3-Silesian Moravia as structural guidance. On the other side, as a genuine contribution from the urban scale, Ostrava´s brand new policy on talent management will enrich the policy-mix supporting the RIS3 at regional level.
The way forward
To summarise, there is still potential to exploit regarding the contribution of cities (local authorities and their relevant subsidiaries) to RIS3 implementation. The best way to do so is not to replicate the RIS3 method automatically top-down to the local level, as this would probably lead to more fragmentation, but rather to bridge with the existing RIS3 strategies, in a kind of two-way bridge, where some innovative cities may enrich strategies as well. As well as providing a bridge with RIS3 at regional level within a vertical multi-governance approach, smart specialisation as a concept is so powerful that it can be used by cities as a crosscutting approach to boost their own work agendas on economic development.
Bilbao, the InFocus lead partner, is a good example of how to operationalise the involvement of cities as smart specialisation practitioners. In 2014, Bilbao Ekintza, the local development agency, made a step forward and organized a cluster prioritization exercise at city level, with an eye on the Basque Country RIS3. It was named “Innovation and intelligent specialisation strategy for Bilbao”. As a main result 6 domains were identified at the time and prioritized in a dynamic way according to their level of consolidation as real business frameworks: Knowledge Intensive Business Services (KIBS), Tourism, Urban Solutions, Arts & Culture, Ecotechnology and Technologies applied to Health. In parallel, the city´s economic development policy-mix was revised, emphasizing a number of working areas such as business cooperation and clustering, entrepreneurship and attraction of investment and knowledge.
At present, within the URBACT-InFocus framework, Bilbao is going further in two mutually reinforcing directions: i) promoting more fluid and in-depth interaction with Basque RIS3; ii) and focusing on three domains out of the six above mentioned: advanced tertiary (KIBS), creative economy and digital economy, also exploring the connections among them, i.e. turning Bilbao-based KIBS sector into an engine for digital transformation, in particular regarding advanced manufacturing which is Basque RIS3´s most significant priority. In practical terms, the aim is to promote and facilitate a pipeline of projects in those domains and in close alignment with the RIS3.
To achieve this objective, Bilbao Ekintza has set up a new collaborative platform by bringing together the following necessary contributors: multi-level governance (Basque Country RIS3 management team and Diputación Foral de Bizkaia as a body with funding capacity), research centres and think tanks (Tecnalia-Technology Corporation and Orkestra-Basque Institute of Competitiveness), private sector and cluster organisations (Chamber of Commerce, IT cluster GAIA, EIKEN audiovisual and AVIC engineering and consultancy) and public and private Universities (UPV/EHU, University of Deusto and Mondragón University).
This collaborative platform is none other than the URBACT Local Group (ULG) the City of Bilbao has established in the frame of InFocus. The ULG is proving to be an effective tool to engage RIS3 regional authorities in a fruitful dialogue with the city. Other InFocus partner cities like Porto, Bucharest or Frankfurt are following in this path and more results of the approach will be shared in the Integrated Action Plans to be launched in 2018.
***
Image 3: InFocus thematic workshop, Ostrava, September 2016
Image 4: Smart specialisation as a driver to refine the urban agenda on business-led economic development
 Submitted by Miguel Rivas on
Submitted by Miguel Rivas on




