9 European cities acting together to end homelessness. Ambitious? Hell, yes!
Edited on
26 August 2020What is homelessness, why is it growing and how innovative housing solutions are bringing it to an end.

Homeless people are increasing in all European countries except one: Finland. The most extreme form of poverty is becoming ever more urgent to tackle. Cities are struggling with understanding the numbers they deal with, define their specific problem and finally find innovative solutions to work with. A time of crisis calls for radical answers and a shift in mind-set. Can the collaboration between 9 European cities lead towards the end of an era?
“I see this lady, just outside the centre where they distribute methadone. Every morning she stands there. She is old and not in a good shape. I have been walking past her every day for the last year; -a whole year, every day. Now we wave hello to each other. She reminds me of why I do my job”. Says Steven as we walk away from the MSOC in Ghent, a medical centre where people can get methadone and support. Steven Vanden Broucke has been working for the Belgian city of Ghent since 2018 and is working on a local action plan to end chronic homelessness. 200 people arrive at the MSOC every day suffering from drug dependency and often mental disease. About half of them are homeless. “Not all of them are without a roof,” tells us one of the project medical doctors “but many live in insecure, inappropriate housing or couch surf.”
The city of Ghent (BE) has the challenging role of leading the new Action Planning Network ROOF in the URBACT program. ROOF is focusing on ending homelessness through innovative housing solutions. The project is a partnership between 9 cities: Ghent (Lead partner), Braga (PT), Glasgow (UK), Gothenburg (SE), Liège (BE), Naples (IT), Timisoara (RO), Thessaloniki (EL) and Toulouse (FR). The cities will compare best and worst practices, learn from one another and grow together with two main objectives: 1. gather accurate data about homelessness in their own city 2. make the shift from managing to the actual ending of homelessness, with Housing First and Housing Led as guidance model.
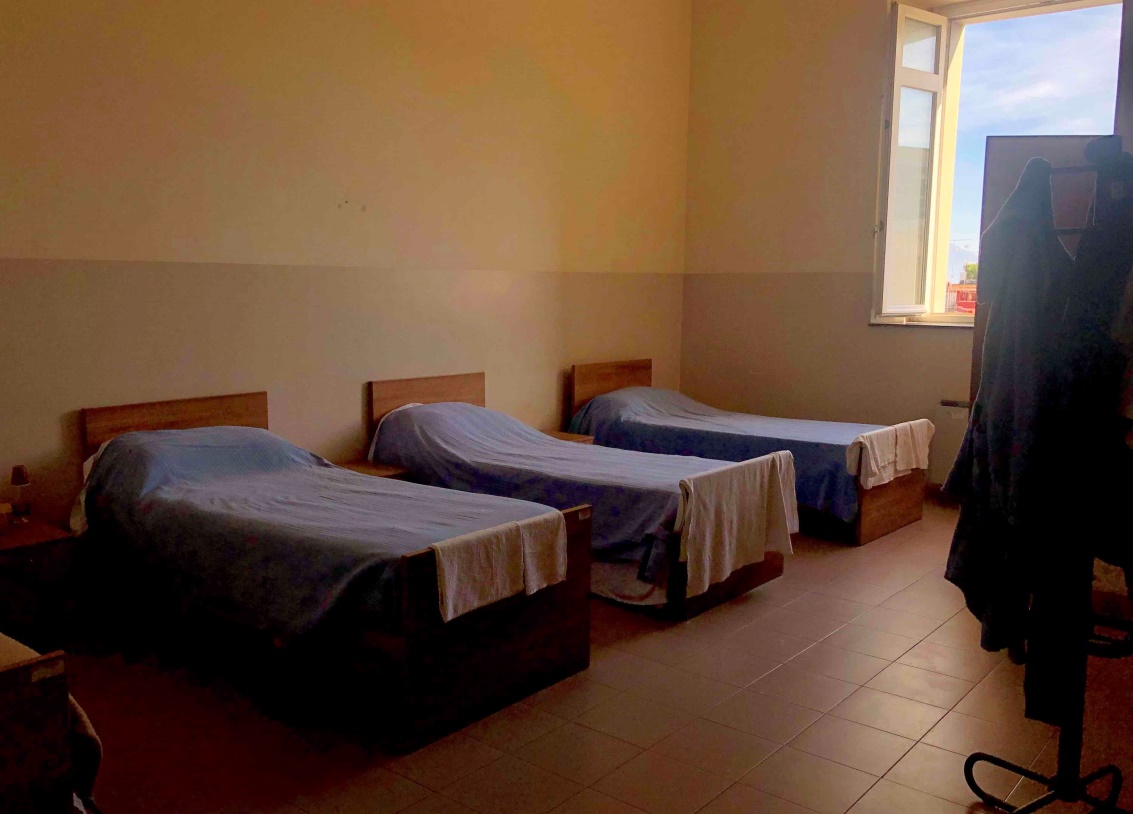

Room in a homeless shelter in Naples (Italy)
To measure is to know
Homelessness does not have one single definition, and this lack of definition is also part of the problem. While the common image of a homeless person is a person living in the streets, many homeless people are sleeping with friends or relatives, in their cars or in unsuitable conditions. Homeless people often do not want to be seen. When visiting one of the day shelters for the homeless in Liège, the director explained: “The people coming to our service to get a meal and a bed, may remain anonymous. We only ask them to maintain the same identity for the whole season.” Patricia Vanderbauwhede who works for the Housing Department of the city of Ghent and ROOF project leader, is certain that an accurate data collection on homelessness is a crucial step towards solving the problem. “It is very convenient for a city to think the numbers are smaller than they really are. We have to work together in order to make this problem visible and reveal the real numbers”.

Even though the numbers are difficult to collect and compare, studies show that more than 4 million people are affected by homelessness each year in Europe. "Only crisis -actual or perceived- produces real change" said Milton Friedman. And for homelessness, the multiple crisis level is evident: the Global Financial Crisis brought higher levels of poverty; the Housing Crisis today makes the housing market become highly inaccessible for most vulnerable people and the European migrant crisis causes difficulty for migrants in finding affordable housing and a homelessness risk, due to their complex situation (such as lack of finances, language barriers, cultural differences, (mental) health issues.
Street art in Sanità neighbourhood in Naples (Italy)
The house as a human right, not a reward.
The ROOF project will not stop at understanding the problem but will explore innovative housing solutions, and especially “Housing First”. The reasons for that come from the observation of, -the only European country showing positive trends on homelessness. It is the only country with a long and successful experience with “Housing First”. The traditional model is a staircase model, where people have to go through several steps before they can get a house, for example by curing their addiction first. In “Housing First”, to be given a home is a first step. Once one has a home, other problems are taken care of, with freedom of choice and flexibility. This puts the house as a human right and not as a reward. Temporary solutions in housing are often unsuccessful for people with complex needs. I met three young adults in Queens Cross housing association in Glasgow during my city visit. “I am very easily influenced,” one of them shared, “going back to an institution or a temporary housing solution, and living with other people that have similar problems would have meant going back to drugs, losing my job… I needed my own space, I needed to put my life together, on my own.” The three young adults now live in small and independent apartments, and have 24/7 support from the housing association if needed.

Study visit to Glasgow (Scotland)
The URBACT framework is perfect for this network, it facilitates exchange and learning on transnational and local level, it offers capacity building, it provides cities with guidance to make a local action plan together with their stakeholders and puts focus on communication and dissemination. These four aspects make a great opportunity for the cities to act. “URBACT allows each city to have a spotlight on a desired topic, to bring it to the political agenda and to the citizens’ attention,” says Ariana Tabaku, from the coordination team of the City of Ghent. “All cities should use this opportunity strategically.”
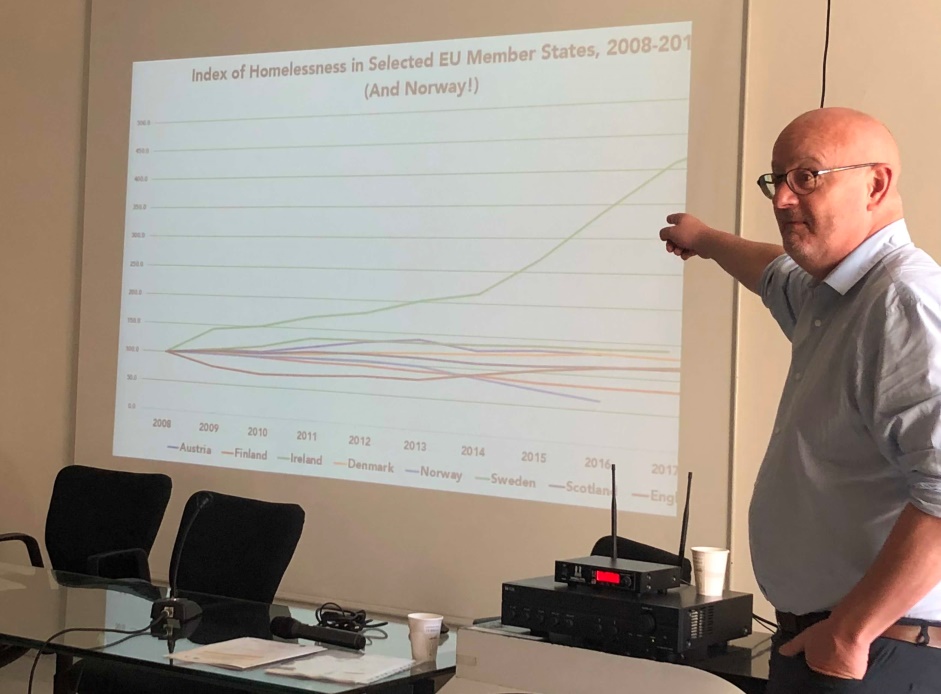
Professor Eoin O'Sullivan (Trinity College, Dublin) speaks at ROOF kick-off meeting
The ROOF network is determined to influence the European strategies on the topic. Europe does not have a specific policy for homelessness. During the network Kick-off Meeting in Naples this October, Professor Eoin O’Sullivan spoke about the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development with one of its aims to reduce homelessness to functional zero (meaning homelessness is rare, brief and non-recurrent) in all member states by 2030. Action plans of 9 cities and small scale solutions in the next two years, may well serve the ambitious aim to end homelessness.
 Submitted by Liat Rogel on
Submitted by Liat Rogel on




